The manufacture of prototypes is crucial for subsequent successful industrialisation
Any product industrialisation strategy goes through a series of critical phases, one of which stands out above all others: prototyping. The manufacture of prototypes to carry out the necessary preliminary tests is a critical moment for any company. After all, a prototype is nothing more than an initial or preliminary model of a product, system or process that is being developed. In other words, a simplified and partial representation of the final product, designed to evaluate its feasibility, functionality, effectiveness and efficiency before the full product is produced.
Logically, this phase is the one that undergoes the greatest number of tests, checks and modifications, as industrialising a product without having carried out the relevant tests is a strategy that is doomed to fail miserably. For this reason, today we are going to try to unravel the secrets of prototyping and its technological and economic importance.
First of all, it should be noted that prototypes can be of different types. From physical prototypes (such as models or scale models) to digital prototypes (such as virtual models or computer simulations). Technology plays an important role in their development. Prototyping is nothing more than a process of technological innovation applied to a specific problem that is being addressed. It allows designers and developers to create and test a preliminary version of a product before investing in full-scale production.
This is why this initial development phase allows problems to be identified and improvements to the product design to be made without incurring significant costs. Imagine having to develop a mass-produced product in order to test whether or not it is viable from a technological and market point of view. Think of a company that wants to launch a vehicle on the market and does so massively without first developing a prototype based on the application of the relevant industrial, technological and design changes. It would be suicide, wouldn’t it? That is the crucial role of any prototyping phase. This also subjects the solution to the evaluation of the human factor represented by the company’s own interests or those of its customers, thus improving the user experience. All this also means a huge saving of time and money in the production phase, as it does not require industrial scaling to be tackled.
In short, prototypes are used as a test bed during the design and development phase of products in order to test them thoroughly.
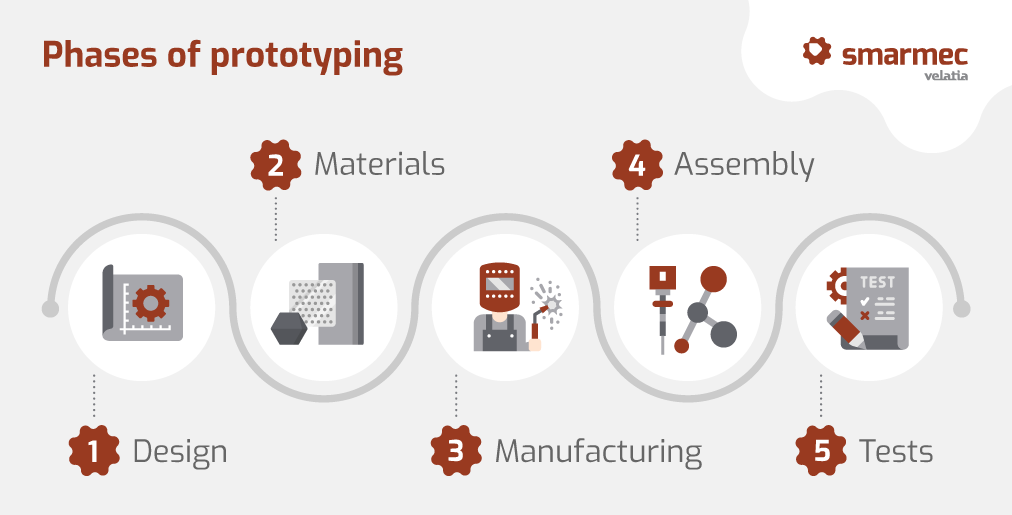
Phases of prototyping
Although, as is logical, there is no single process for manufacturing a prototype, but rather it is adapted according to the typology and characteristics of the future product, we can distinguish a series of more or less generic phases. These can be summarised in the following points:
- Design: The first step in the manufacture of prototypes is to create a detailed design of the product using computer-aided design (CAD) software or manual design tools. The design should include all the features and details needed for the prototype.
- Material selection: after creating the design, the materials to be used to manufacture the prototype must be selected. Depending on the type of prototype, materials such as plastics, metals, wood, foam, among others, can be used.
- Manufacturing: once the materials have been selected, the prototype is manufactured. This process can involve different manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or laser cutting, among others. The aim is to create a visual representation of the product.
- Assembly: Once all the parts of the prototype have been manufactured, they are assembled. At this stage, all the parts are put together to create a functional representation of the product.
- Testing and adjustment: Finally, the prototype is tested to assess its functionality and to detect any problems or flaws in the design. If problems are detected, the design is adjusted and the manufacturing and assembly process is repeated until a satisfactory version of the prototype is achieved.
Smarmec, proven experience in prototype manufacturing
The agility of an organisation is a fundamental factor in the fabrication of prototypes. After the design and development phases of a product, we work on prototyping and its evaluation. The purpose of this process is to notice possible problems or discover potential improvements, both from a manufacturing and business point of view.
In fact, it is very common to find a mistake which means changes or even the construction of new prototypes until the final one is found. This is a very important phase as it avoids future uncertainties, which is why the flexibility of our organisation is key during this process.
The prototyping phase consists of making tangible the ideas that come from the previous design phases. At Smarmec, we assess the maturity and complexity of a design in order to advise the client on the manufacture of a prototype.
Do you want to know more?